Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
What are the common failure modes of zipcord Interconnect fiber optic cable?
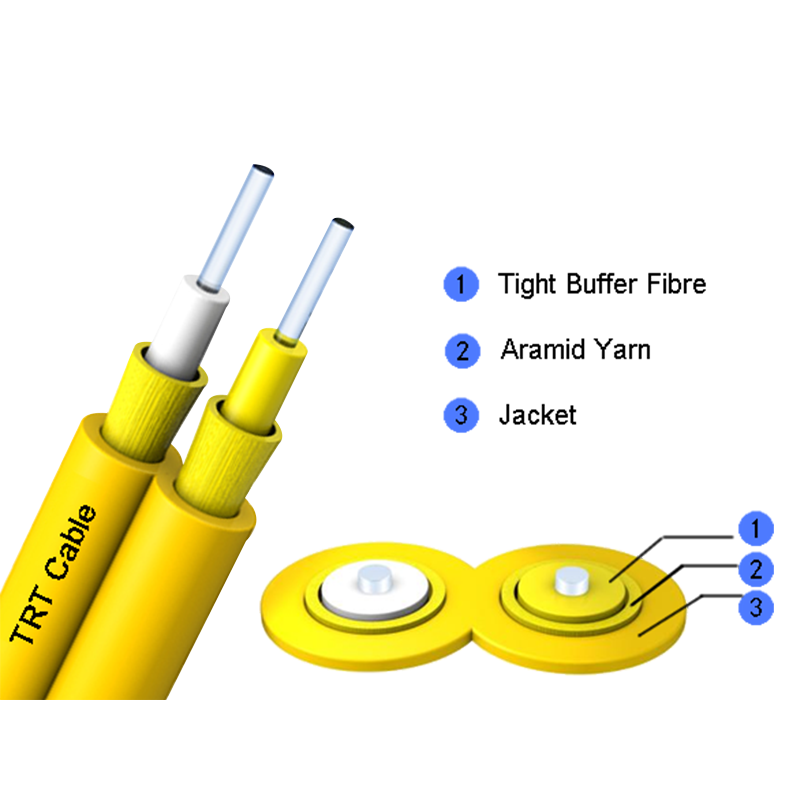
What are the common failure modes of zipcord Interconnect fiber optic cable?
The zipcord Interconnect fiber optic cable is a widely used component in telecommunications, data centers, and networking environments due to its simplicity, compact design, and flexibility. Despite its advantages, this type of fiber optic cable can experience various failure modes that affect performance, signal integrity, and operational reliability.
Mechanical stress and fiber breakage
One of the most frequent failure modes in zipcord Interconnect fiber optic cable is mechanical stress. The fibers within these cables are sensitive to bending, tension, and crushing. Excessive mechanical force can cause micro-cracks or complete breakage of the optical fiber core, leading to signal loss or complete disconnection.
Mechanical stress can arise from several sources:
- Improper handling during installation
- Excessive pulling or tension while routing the cable
- Sharp bends or tight loops exceeding the recommended bend radius
- Pressure from mounting clips, conduits, or storage methods
Symptoms of fiber breakage often include intermittent signal loss, attenuation spikes, or complete loss of connectivity in one or both fibers of the zipcord. To mitigate mechanical stress failures, technicians are advised to:
- Maintain proper bend radius as specified by the manufacturer
- Use fiber-specific pulling grips and lubricants
- Avoid kinking or compressing the cable during installation
- Implement strain relief at connection points
Table 1 provides an overview of typical mechanical stress failure scenarios in zipcord cables:
| Failure Scenario | Cause | Observed Effect | Preventive Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Micro-bend in fiber | Tight loops or excessive bending | Signal attenuation increase | Maintain bend radius and routing guidelines |
| Fiber breakage | Excessive pulling tension | Complete signal loss | Use pulling grips and strain relief |
| Crush damage | Heavy pressure or sharp edges | Permanent fiber deformation | Avoid tight clamps, use protective conduit |
Connector and termination issues
Connector failures are another critical factor in zipcord cable reliability. Since the zipcord Interconnect fiber optic cable typically terminates with SC, LC, or ST connectors, poor termination can significantly impair performance. Common connector-related failure modes include:
- Misalignment of fiber cores during termination
- Contaminants such as dust or oils on connector end faces
- Improper polishing of fiber end surfaces
- Loose or poorly secured connector housings
Such issues manifest as high insertion loss, elevated return loss, or unstable connectivity. Routine inspection and cleaning are essential. Recommended practices include:
- Using proper fiber cleaning tools such as lint-free wipes and isopropyl alcohol
- Employing visual inspection microscopes for end-face verification
- Following manufacturer-approved termination procedures
Table 2 summarizes common connector and termination failure modes:
| Failure Mode | Cause | Detection Method | Preventive Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Misalignment | Improper termination | OTDR or power meter measurement | Ensure precise alignment during termination |
| Contamination | Dust, oils, or debris | Visual inspection | Clean connectors before mating |
| Poor polishing | Inadequate polishing technique | Reflection or loss testing | Use manufacturer-approved polishing tools |
| Loose connector housing | Connector not properly secured | Wobble or intermittent loss | Tighten or replace connector housing |
Environmental factors
The zipcord Interconnect fiber optic cable is also susceptible to environmental stress. Temperature fluctuations, humidity, UV exposure, and chemical contact can lead to cable degradation over time. Specific examples include:
- Thermal expansion or contraction: Repeated temperature changes can cause microbending and increased attenuation.
- Moisture ingress: Humidity or water exposure may penetrate the cable jacket, compromising fiber integrity.
- UV degradation: Prolonged exposure to sunlight can deteriorate the jacket material, especially if the cable is intended for indoor use.
- Chemical exposure: Contact with solvents, oils, or cleaning agents can weaken the polymer jacket or buffer layer.
Preventive strategies involve using the appropriate cable type for environmental conditions, including indoor-rated, outdoor-rated, or UV-resistant zipcord cables, and installing protective conduits or cable trays.
Bend radius and handling-related failures
Improper bending is a common contributor to zipcord Interconnect fiber optic cable failures. These cables are designed with a specific minimum bend radius, typically indicated by the manufacturer. Exceeding this radius can cause:
- Microbending, which increases attenuation
- Macrobending, potentially resulting in fiber breakage
- Permanent deformation of the buffer or jacket
During installation, care should be taken to route the cable around corners smoothly, avoid sharp bends, and maintain gradual curves. Cable management solutions such as fiber guides, raceways, and bend limiters help preserve cable integrity.
Signal attenuation and performance degradation
Over time, a zipcord Interconnect fiber optic cable may exhibit performance degradation even without mechanical damage. Common causes include:
- Aging of the fiber material
- Repeated flexing or vibration
- Connector contamination or micro-scratches
Symptoms are usually observed as gradual signal attenuation, increased bit error rate, or intermittent connectivity issues. Preventive maintenance, including periodic inspection, cleaning, and testing, helps sustain optimal performance.
Installation and routing errors
Incorrect installation and routing practices often result in mechanical or optical stress. Common issues include:
- Exceeding maximum allowable pull tension
- Routing cables through high-traffic areas without protection
- Twisting or tangling multiple zipcord cables together
Addressing these issues involves careful planning of cable pathways, adherence to manufacturer specifications, and proper labeling for maintenance purposes.
Rodent and pest damage
While less common indoors, rodent damage can occur in certain environments. Rodents may chew the jacket of a zipcord Interconnect fiber optic cable, exposing the fiber and causing signal failure. Preventive methods include:
- Using rodent-resistant conduits or protective sheaths
- Inspecting and securing cable pathways in susceptible areas
Summary of common failure modes
The failure modes discussed can be categorized as follows:
- Mechanical stress – bends, tension, crushes
- Connector and termination issues – misalignment, contamination
- Environmental factors – temperature, moisture, UV, chemicals
- Handling and routing errors – improper bend radius, installation mistakes
- Signal attenuation and performance degradation – aging, microbends, flexing
- Rodent and pest damage – physical chewing or penetration
Understanding these categories allows technicians to proactively implement preventive measures, reducing downtime and enhancing network reliability.
Best practices to minimize failures
To maintain the integrity and performance of zipcord Interconnect fiber optic cable, the following best practices are recommended:
- Adhere to installation guidelines, including bend radius and pull tension limits
- Clean and inspect connectors regularly
- Use appropriate cable types for environmental conditions
- Implement protective routing solutions such as conduits and cable trays
- Perform periodic testing using optical power meters or OTDR devices
- Label and document cable pathways to reduce handling errors during maintenance
Table 3 – Recommended preventive measures
| Failure Type | Recommended Action | Frequency/Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical stress | Use bend limiters, avoid tight bends | During installation |
| Connector contamination | Clean with lint-free wipes and alcohol | Before mating or quarterly maintenance |
| Environmental exposure | Use outdoor/UV-rated cables and protective conduits | Continuous |
| Signal degradation | Test using OTDR and monitor attenuation | Periodically or during network audits |
| Rodent damage | Install protective conduits | In susceptible areas |
Conclusion
The zipcord Interconnect fiber optic cable is a reliable and versatile solution for a wide range of network applications. However, understanding its common failure modes—including mechanical stress, connector issues, environmental factors, and handling errors—is essential for maintaining long-term network performance. By implementing preventive measures and adhering to best practices, network professionals can minimize failures and ensure consistent optical performance.
FAQ
Q1: How can I detect a broken zipcord Interconnect fiber optic cable?
A1: Broken fibers typically result in intermittent signal loss or complete disconnection. Detection can be performed using an optical time-domain reflectometer (OTDR) or a visual fault locator.
Q2: What is the recommended bend radius for zipcord Interconnect fiber optic cable?
A2: The recommended bend radius is usually 10 times the cable diameter for single-mode and 15 times for multi-mode fibers, but it is best to follow the manufacturer’s specification.
Q3: How often should I clean zipcord Interconnect fiber optic cable connectors?
A3: Connectors should be cleaned before every connection and periodically, typically every three to six months in high-use environments.
Q4: Can zipcord Interconnect fiber optic cable be used outdoors?
A4: Standard indoor zipcord cables are not designed for prolonged outdoor exposure. Use outdoor-rated or UV-resistant cables for external applications.
Q5: What is the main cause of attenuation in zipcord Interconnect fiber optic cable?
A5: Attenuation can result from microbends, macrobends, connector contamination, or fiber aging. Regular inspection and testing help mitigate these issues.
References
- Keiser, G. (2020). Optical Fiber Communications. McGraw-Hill Education.
- Senior, J. M., & Jamro, M. Y. (2021). Optical Fiber Communications: Principles and Practice. Pearson.
- Agrawal, G. P. (2022). Fiber-Optic Communication Systems. Wiley.
 Address:Zhong'an Road, Puzhuang Town, Suzhou City, Jiangsu Prov., China
Address:Zhong'an Road, Puzhuang Town, Suzhou City, Jiangsu Prov., China Phone:+86-189 1350 1815
Phone:+86-189 1350 1815 Tel:+86-512-66392923
Tel:+86-512-66392923 Fax:+86-512-66383830
Fax:+86-512-66383830 Email:[email protected]
Email:[email protected] Wechat: xiaobin18913501815
Wechat: xiaobin18913501815 whatsapp: +86 18913501815
whatsapp: +86 18913501815
 0
0

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español Português
Português عربى
عربى