Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
How does the cable design of Self-supporting Round fiber optic cable prevent water ingress?
How does the cable design of Self-supporting Round fiber optic cable prevent water ingress?
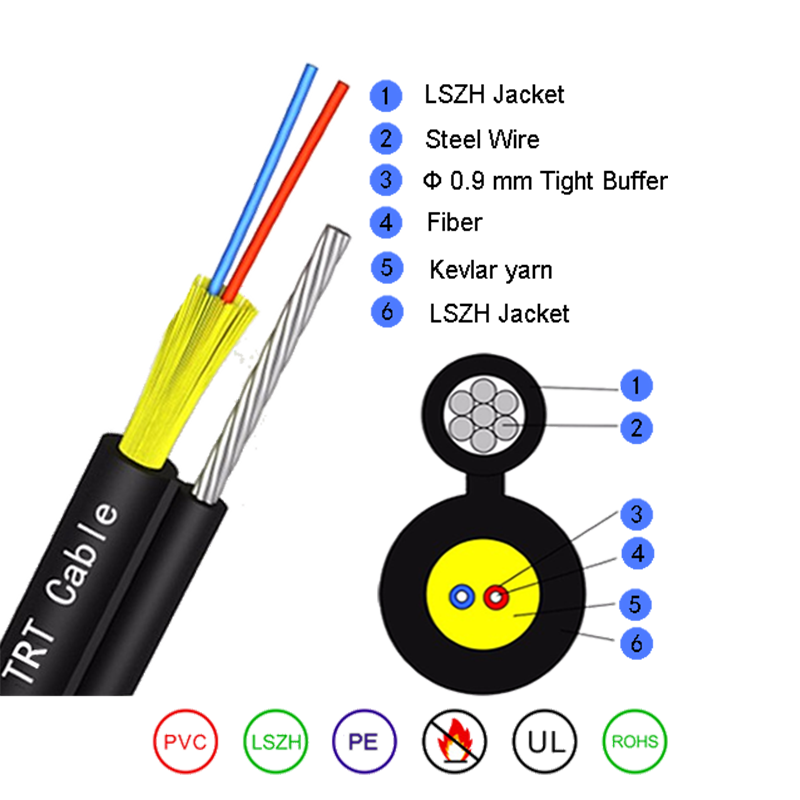
Self-supporting Round fiber optic cable has become a critical component in modern fiber optic networks, particularly for outdoor and aerial applications. Its design addresses many environmental challenges, with water ingress prevention being one of the most significant concerns.
Understanding Self-supporting Round fiber optic cable
Self-supporting Round fiber optic cable is designed to combine the transmission of high-speed optical signals with mechanical strength to support aerial installations without additional support. Unlike conventional fiber optic cables that may require messenger wires or conduits, these cables are engineered to sustain tension over long spans.
Key features of Self-supporting Round fiber optic cable include:
- Durable outer jacket materials that protect fibers from environmental exposure.
- Reinforcing elements such as aramid yarn, which enhance tensile strength.
- Water-blocking mechanisms integrated into the cable core to prevent moisture migration.
The combination of these features ensures that the cable remains operational even under challenging conditions such as rain, snow, ice, and high humidity.
Why water ingress is a critical concern
Water ingress can significantly compromise the performance and longevity of optical networks. When water enters a fiber optic cable, it can lead to several issues:
- Increased attenuation, which reduces signal quality.
- Degradation of internal components such as fibers and strengthening materials.
- Ice formation in colder climates, causing mechanical stress on fibers.
- Accelerated corrosion or chemical reactions in certain cable elements.
For network operators and installers, preventing water ingress in Self-supporting Round fiber optic cable is essential to maintain consistent data transmission quality and reduce maintenance costs.
Cable design elements for water ingress prevention
The ability of Self-supporting Round fiber optic cable to resist water ingress is largely determined by its design. Several technical elements contribute to this protection:
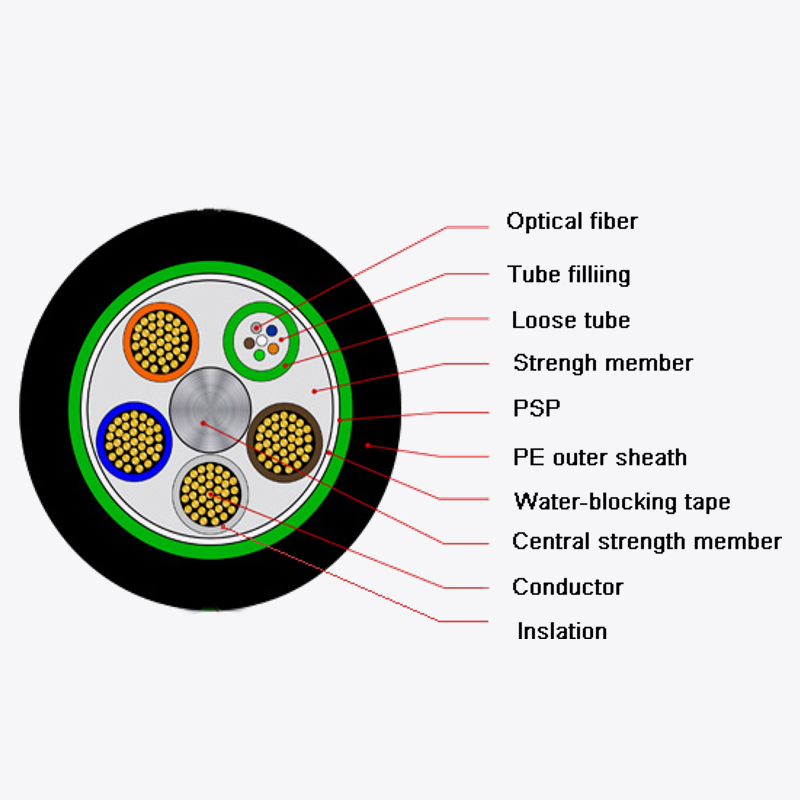
1. Water-blocking materials
One of the primary strategies for preventing water ingress is the use of water-blocking materials inside the cable. These materials can take several forms:
- Water-blocking yarns or threads: These are usually made from super-absorbent polymers (SAP) that swell when they come into contact with water, sealing gaps and preventing further migration.
- Gel-filled cores: Some designs include a gel that surrounds the optical fibers, filling spaces and acting as a barrier to water.
- Water-blocking tapes or tapes with swelling powders: These are applied in layers around the fiber bundles to prevent longitudinal water movement.
These materials ensure that even if water penetrates the outer jacket, it cannot travel along the cable core and reach the fibers.
2. Fiber buffer and core protection
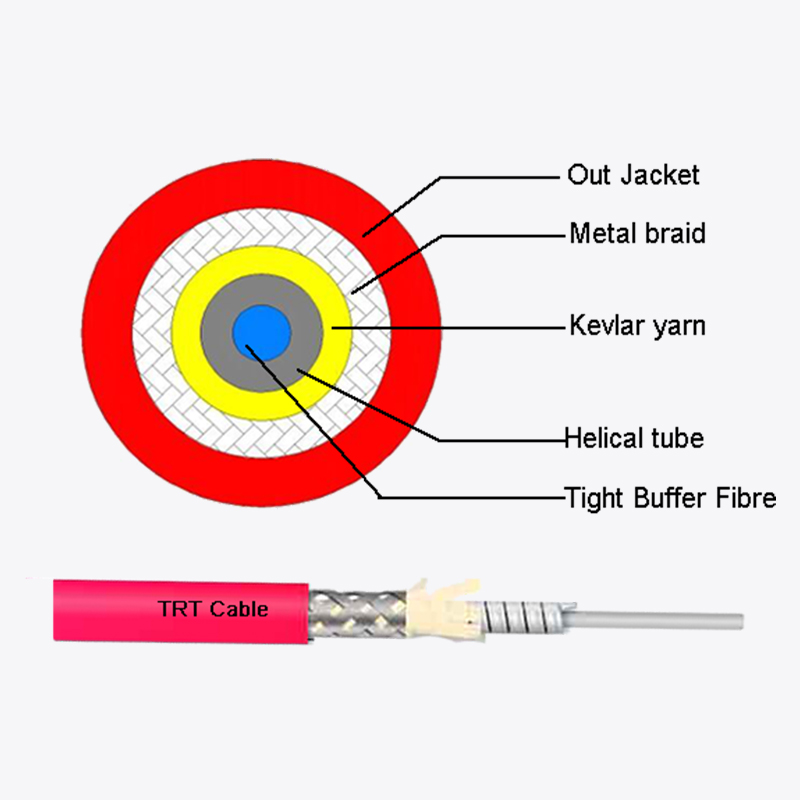
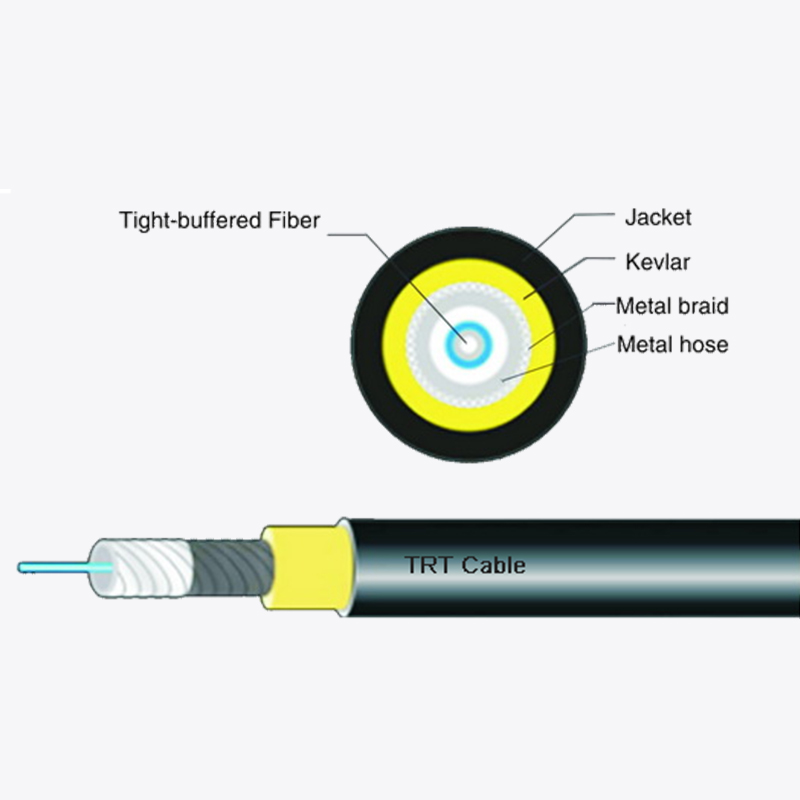
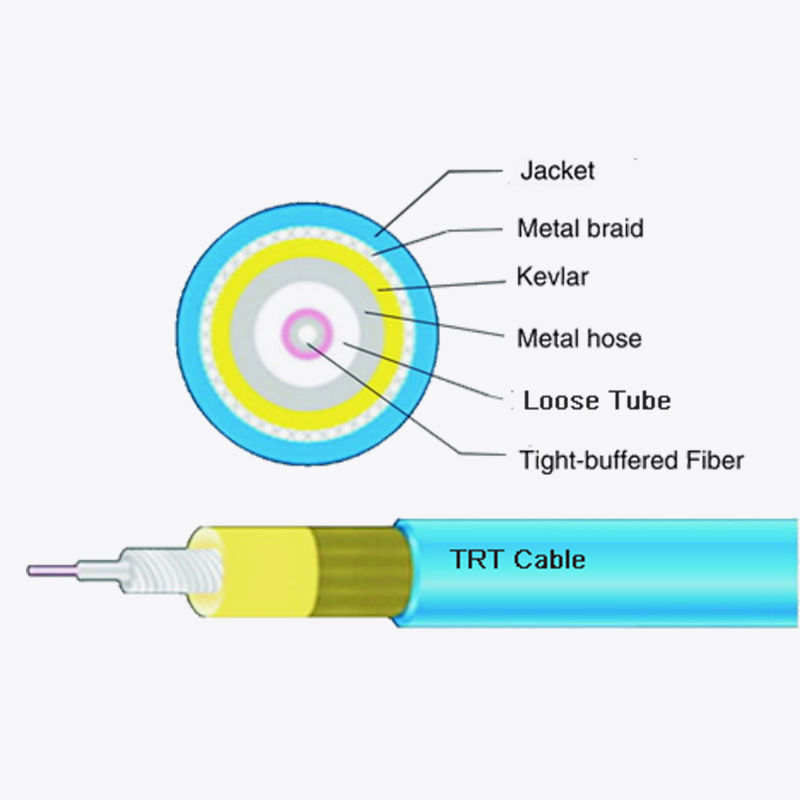
Self-supporting Round fiber optic cable often uses a buffered fiber structure to enhance protection:
- Loose tube fibers: Optical fibers are enclosed within loose tubes filled with water-blocking gel or powder. This prevents direct contact between fibers and potential moisture.
- Central strength members: Many cables include a central reinforcing element, which may also help limit water migration along the cable’s axis.
This structural design isolates each fiber or fiber bundle from environmental exposure while maintaining flexibility and ease of installation.
3. Reinforced outer jacket
The outer jacket of Self-supporting Round fiber optic cable serves as the first line of defense against environmental elements. Key characteristics include:
- UV-resistant polymers that prevent degradation from sunlight.
- Moisture-resistant materials such as polyethylene (PE) or low-smoke zero-halogen (LSZH) compounds.
- Dense sheathing and minimal seam designs, which reduce entry points for water.
The combination of material selection and physical design ensures that water cannot easily penetrate the cable from the outside.
4. Aerial self-supporting features
Since Self-supporting Round fiber optic cable is often installed aerially, mechanical design considerations also help prevent water ingress:
- Tension members: Aramid yarns or fiberglass rods not only provide tensile strength but also support proper cable geometry, reducing bending points where water could accumulate.
- Round cross-section design: A circular profile helps shed water naturally, reducing the likelihood of prolonged water contact.
- Properly sealed end caps and closures: Ensuring that cable terminations are water-tight complements the internal water-blocking design.
Together, these elements reduce the opportunity for water to enter and move along the cable.
Installation practices that enhance water resistance
Even the best cable design can be compromised if installation practices are poor. To maximize water ingress prevention in Self-supporting Round fiber optic cable, installers should consider the following:
- Maintain proper tension during aerial installation to prevent sagging, which can create water-collection points.
- Avoid sharp bends near support structures, which can compromise the integrity of the outer jacket.
- Use water-tight closures at splice points and terminations to complement the cable’s internal water-blocking features.
- Inspect cable before installation for any physical damage that could create moisture entry points.
By combining thoughtful design with careful installation, network operators can significantly reduce the risk of water-related failures.
Environmental factors and durability
Self-supporting Round fiber optic cable is designed for a range of environmental conditions. Its water-blocking design must be effective in:
- High rainfall areas, where prolonged exposure to moisture can challenge the cable jacket.
- Cold climates, where freezing water can expand and damage fibers.
- Coastal regions, where saltwater and high humidity increase corrosion risks.
The durability of these cables depends not only on the materials and design but also on routine inspection and maintenance practices to identify potential wear points before water ingress occurs.
Maintenance and inspection considerations
Preventing water ingress is not only about initial design but also ongoing cable health management. Recommended practices include:
- Periodic visual inspections of aerial spans for jacket integrity.
- Testing for optical loss or attenuation, which may indicate early water intrusion.
- Monitoring environmental conditions, such as proximity to water sources or exposure to ice and snow accumulation.
Proactive maintenance helps ensure that Self-supporting Round fiber optic cable continues to perform optimally over its expected service life.
Benefits of water-resistant design
The robust water-blocking features of Self-supporting Round fiber optic cable provide several practical benefits for network operators:
- Extended service life, reducing the need for premature replacements.
- Lower maintenance costs, as water-related faults are minimized.
- Reliable network performance, ensuring high-speed data transmission even under adverse weather conditions.
- Versatility in deployment, allowing use in aerial, underground, or hybrid environments.
These advantages make Self-supporting Round fiber optic cable a preferred choice for many outdoor optical network applications.
Common user search terms and related keywords
When discussing Self-supporting Round fiber optic cable, it is useful to integrate commonly searched industry and buyer terms to improve visibility and relevance:
- Aerial fiber optic cable
- Water-blocking fiber optic cable
- Outdoor fiber optic cable installation
- Loose tube fiber optic cable
- Tensile strength fiber optic cable
- UV-resistant fiber optic cable
Incorporating these terms naturally into content helps address the questions and concerns of potential buyers and network engineers.
Summary
The cable design of Self-supporting Round fiber optic cable effectively prevents water ingress through a combination of internal water-blocking materials, reinforced outer jackets, fiber buffer protection, and aerial installation features. Careful installation and maintenance further enhance this protection, ensuring long-term network reliability.
By understanding the design features, environmental considerations, and installation best practices, buyers and network operators can make informed decisions that maximize the performance and longevity of their fiber optic infrastructure.
 Address:Zhong'an Road, Puzhuang Town, Suzhou City, Jiangsu Prov., China
Address:Zhong'an Road, Puzhuang Town, Suzhou City, Jiangsu Prov., China Phone:+86-189 1350 1815
Phone:+86-189 1350 1815 Tel:+86-512-66392923
Tel:+86-512-66392923 Fax:+86-512-66383830
Fax:+86-512-66383830 Email:[email protected]
Email:[email protected] Wechat: xiaobin18913501815
Wechat: xiaobin18913501815 whatsapp: +86 18913501815
whatsapp: +86 18913501815
 0
0

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español Português
Português عربى
عربى