Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
How does duct butterfly drop fiber optic cable prevent signal attenuation?
How does duct butterfly drop fiber optic cable prevent signal attenuation?
Duct butterfly drop fiber optic cable is widely used in modern fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) networks and other high-speed communication infrastructures. Signal attenuation, or the reduction in signal strength during transmission, is a critical concern in fiber optic networks. Network reliability, data integrity, and high-speed connectivity depend heavily on the ability of the fiber optic cable to minimize attenuation.
Understanding signal attenuation in fiber optic networks
Signal attenuation occurs when light signals lose intensity while traveling through the fiber. Factors contributing to attenuation include fiber bending, microbending, material impurities, and environmental conditions. Excessive attenuation can compromise network performance, leading to slower data rates, packet loss, and connection instability.
In the context of duct butterfly drop fiber optic cable, attenuation can be mitigated through careful design and material selection. The cable’s tight buffer design and protective structure are key factors in maintaining signal integrity over long distances.
Factors affecting attenuation
Several factors contribute to signal attenuation in fiber optic networks:
- Intrinsic fiber loss: Loss caused by the fiber’s material and optical properties.
- Microbending and macrobending: Small and large bends in the fiber can cause light leakage.
- Connector and splice losses: Improper termination or poor splicing can introduce additional attenuation.
- Environmental stress: Temperature fluctuations, moisture, and mechanical pressure can degrade signal quality.
By addressing these factors, duct butterfly drop fiber optic cable ensures minimal signal degradation.
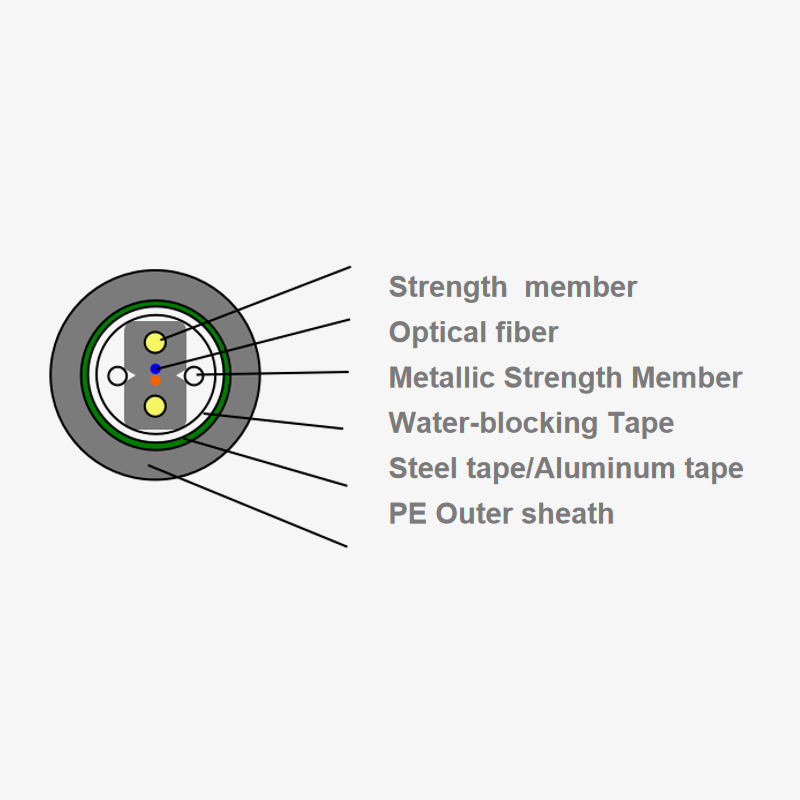
Structural features of duct butterfly drop fiber optic cable
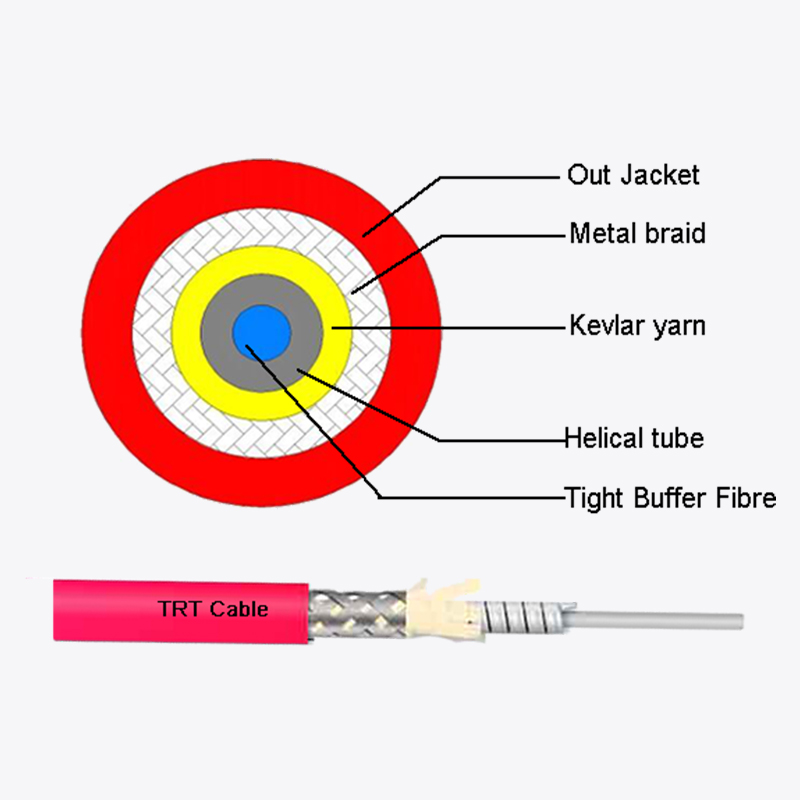
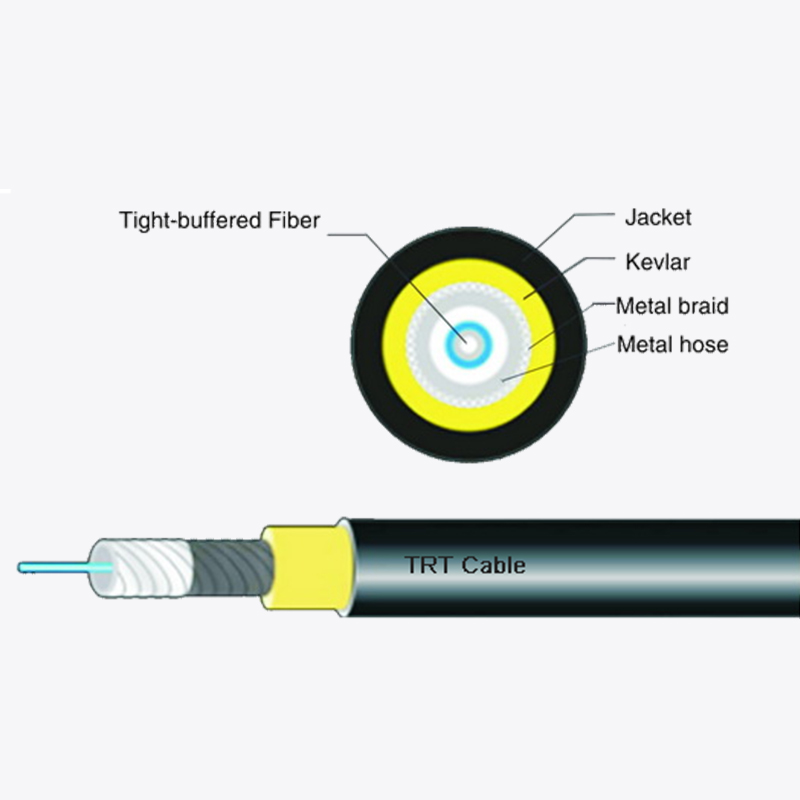
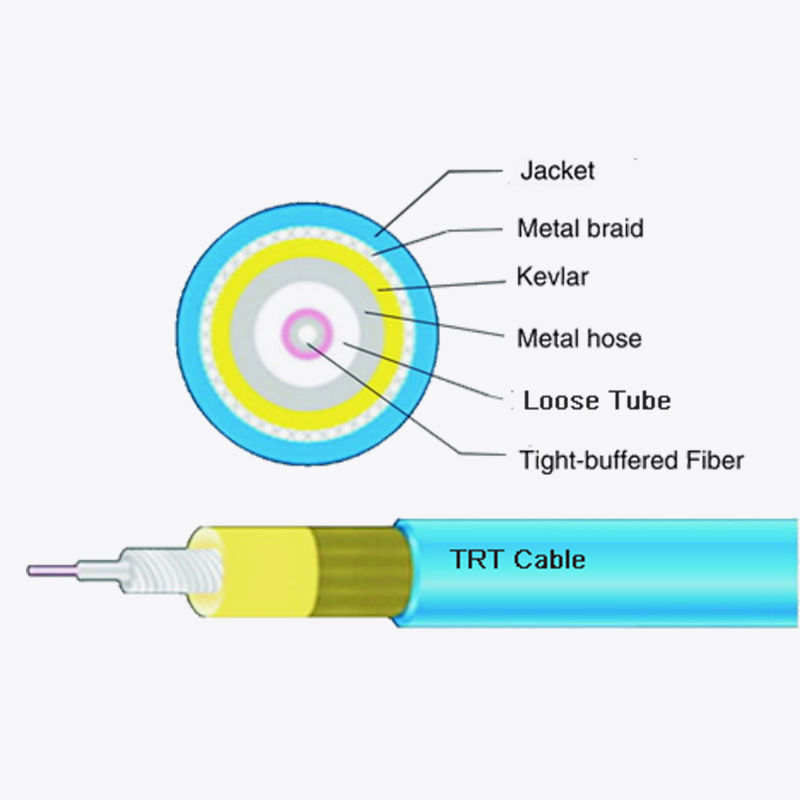
The structure of duct butterfly drop fiber optic cable is optimized for attenuation prevention. Its design incorporates several elements that enhance performance:
- Central strength members: These provide mechanical stability and prevent excessive bending.
- Tight buffer fibers: Each fiber is individually coated to protect against microbending and stress.
- Water-blocking materials: These prevent moisture ingress, which can increase attenuation.
- Outer jacket: Provides protection against environmental and mechanical damage while maintaining flexibility.
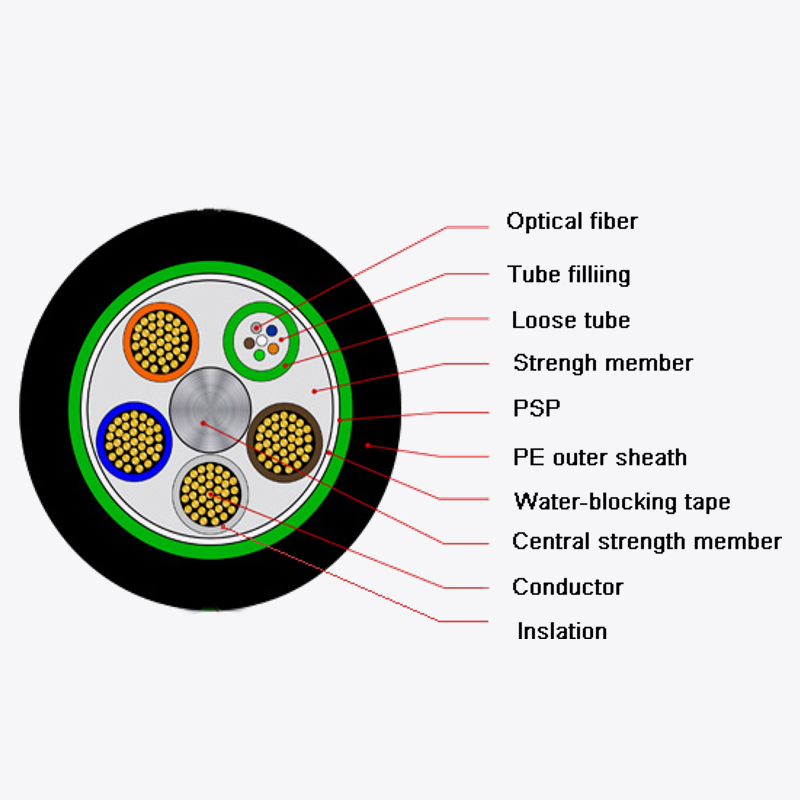
Table 1 illustrates the primary structural components and their functions in preventing signal loss:
| Component | Function in Attenuation Prevention |
|---|---|
| Tight buffer fibers | Protect each optical fiber from microbending and mechanical stress |
| Central strength member | Maintains cable geometry and resists tension during installation |
| Water-blocking material | Prevents moisture penetration that can increase light scattering |
| Outer jacket | Protects against physical damage and environmental hazards |
The combination of these features allows duct butterfly drop fiber optic cable to maintain low attenuation even in challenging deployment scenarios.
Material considerations for attenuation control
The choice of materials in duct butterfly drop fiber optic cable has a direct impact on signal attenuation:
- High-purity optical glass: Reduces intrinsic fiber loss and scattering.
- Polymer coatings: Absorb microbending stress and improve fiber resilience.
- UV-resistant jackets: Protect fibers from long-term environmental degradation.
- Water-blocking compounds: Ensure that the presence of moisture does not increase light loss.
Using materials specifically engineered to address these factors ensures that the cable delivers consistent optical performance over time.
Installation practices that minimize attenuation
Proper installation is as crucial as cable design. Even the best duct butterfly drop fiber optic cable can suffer from signal loss if installation guidelines are not followed. Key considerations include:
- Maintaining bend radius: Avoiding sharp bends prevents macrobending losses.
- Controlled tension: Excessive pulling force during installation can introduce microbends.
- Proper splicing and termination: High-quality connectors and fusion splicing reduce insertion loss.
- Environmental protection: Ensuring cables are installed away from sources of moisture, heat, or physical stress.
Table 2 provides an overview of installation practices and their impact on signal attenuation:
| Installation Practice | Effect on Attenuation |
|---|---|
| Maintaining bend radius | Prevents macrobending losses |
| Controlled tension during pull | Reduces microbending |
| Proper splicing & termination | Minimizes connector loss |
| Environmental protection | Prevents moisture and mechanical stress |
By combining well-engineered cable design with proper installation, duct butterfly drop fiber optic cable can maintain signal integrity over long distances.
Environmental factors and durability
Environmental conditions can significantly impact attenuation. Duct butterfly drop fiber optic cable is engineered to withstand these challenges through:
- Temperature stability: Materials that resist expansion and contraction minimize stress on fibers.
- Moisture resistance: Water-blocking gels or tapes prevent optical degradation.
- Chemical resistance: Protects the cable from external contaminants.
- UV and sunlight protection: Reduces material degradation in outdoor deployments.
These features ensure the cable maintains low signal loss in both indoor and outdoor installations.
Application scenarios
Duct butterfly drop fiber optic cable is commonly used in several high-performance network scenarios, such as:
- FTTH networks: Delivering high-speed internet to residential areas.
- Metropolitan area networks (MANs): Connecting multiple nodes within urban centers.
- Backbone connections: Providing reliable links between distribution hubs.
- Campus networks: Supporting institutional networks with high data demands.
In each scenario, the cable’s attenuation prevention characteristics ensure stable and reliable data transmission.
Advances in duct butterfly drop fiber optic cable technology
Recent developments in duct butterfly drop fiber optic cable technology further improve attenuation prevention:
- Enhanced buffer materials: Better absorption of mechanical stress reduces microbending losses.
- Smaller bend-insensitive fibers: Allow tighter routing without signal degradation.
- Improved water-blocking compounds: Provide superior protection in harsh environments.
- Lightweight and flexible designs: Facilitate easier installation while maintaining performance.
These innovations enhance the cable’s ability to deliver high-bandwidth, low-loss connections.
Conclusion
The ability of duct butterfly drop fiber optic cable to prevent signal attenuation stems from a combination of engineered fiber structures, high-quality materials, and best-practice installation techniques. By protecting fibers from mechanical, environmental, and intrinsic losses, this cable type ensures consistent performance across a variety of network deployments. Proper planning, handling, and installation further optimize the cable’s attenuation prevention capabilities.
Duct butterfly drop fiber optic cable remains a critical solution for modern network infrastructures where low signal loss, high reliability, and long-term durability are essential.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the main reason signal attenuation occurs in fiber optic cables?
Signal attenuation occurs due to fiber bending, material impurities, and environmental factors like moisture and temperature fluctuations.
Q2: How does tight buffering help reduce signal attenuation?
Tight buffering protects each fiber from microbending and mechanical stress, which directly reduces signal loss.
Q3: Can duct butterfly drop fiber optic cable be used outdoors?
Yes, with appropriate jackets and water-blocking materials, it is suitable for both indoor and outdoor deployments.
Q4: How important is maintaining bend radius during installation?
Maintaining the recommended bend radius is crucial to prevent macrobending losses and maintain low attenuation.
Q5: What materials are most effective in preventing signal loss?
High-purity optical glass, polymer coatings, water-blocking compounds, and UV-resistant jackets all contribute to minimizing attenuation.
References
- G. Keiser, Optical Fiber Communications, McGraw-Hill, 2021.
- J. Senior, Optical Fiber Communications Principles and Practice, 4th Edition, Pearson, 2020.
- International Telecommunication Union (ITU-T), Recommendation G.652: Characteristics of a single-mode optical fiber and cable, ITU, 2016.
 Address:Zhong'an Road, Puzhuang Town, Suzhou City, Jiangsu Prov., China
Address:Zhong'an Road, Puzhuang Town, Suzhou City, Jiangsu Prov., China Phone:+86-189 1350 1815
Phone:+86-189 1350 1815 Tel:+86-512-66392923
Tel:+86-512-66392923 Fax:+86-512-66383830
Fax:+86-512-66383830 Email:[email protected]
Email:[email protected] Wechat: xiaobin18913501815
Wechat: xiaobin18913501815 whatsapp: +86 18913501815
whatsapp: +86 18913501815
 0
0

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español Português
Português عربى
عربى