Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
What Makes Bow-Type Drop Cable the Superior Choice for FTTH Aerial Installations?
What Makes Bow-Type Drop Cable the Superior Choice for FTTH Aerial Installations?
The relentless global expansion of Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) networks represents a critical push towards future-proof digital infrastructure. As service providers race to deploy high-speed internet to households, the choice of physical medium for the final connection—the drop cable—becomes paramount. Among the various options available for aerial installation, one design consistently stands out for its efficiency, durability, and economic advantage: the bow-type drop fiber optic cable. This cable’s unique construction is not an arbitrary design choice but a direct response to the practical challenges of outdoor aerial environments. Its superiority is evident from the warehouse to the pole, and throughout its decades-long service life.
Understanding the Anatomy of a Bow-Type Drop Cable
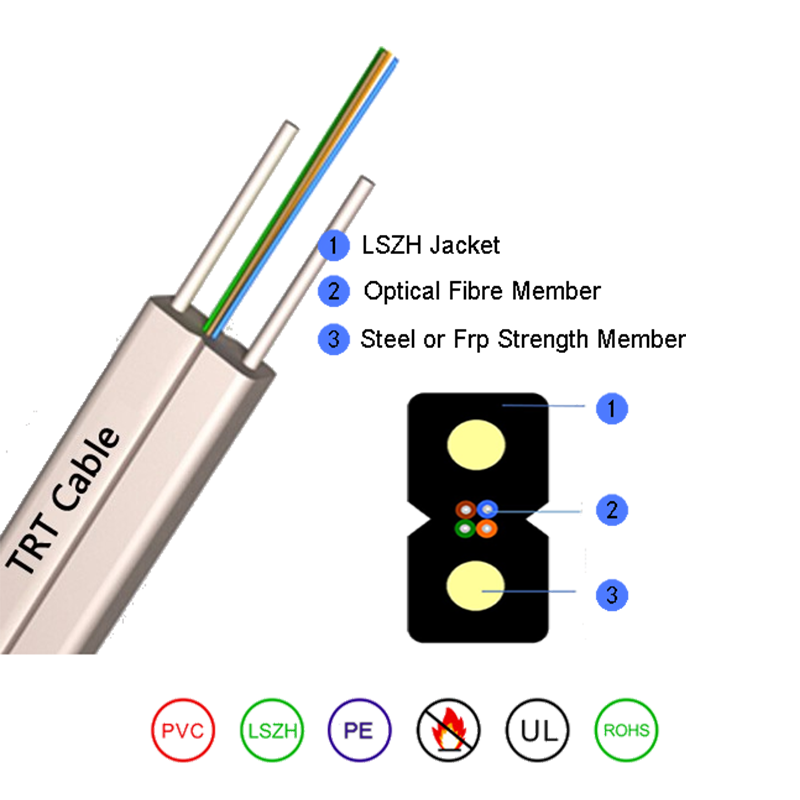
To appreciate its advantages, one must first understand what sets this cable apart structurally. The term “bow-type” is derived from its distinctive cross-sectional profile, which resembles an archer’s bow. This shape is the result of a specific manufacturing process where a messenger wire, typically made of galvanized steel or a dielectric strength member, is laid parallel to the optical fiber unit and then coated with a protective jacket. This process creates a single, integrated cable with a figure-eight-like shape, where the “top loop” is the messenger and the “bottom loop” contains the fiber.
The core components of a standard bow-type drop fiber optic cable include:
- Optical Fiber Unit: At the heart of the cable is the fiber itself, usually one or two single-mode fibers (e.g., G.657.A1 or A2 bend-insensitive fibers) chosen for their compatibility with high-bandwidth applications and resistance to bending losses around poles and eaves. These fibers are typically housed within a loose tube or tight buffered structure, surrounded by a layer of strength yarns like aramid (Kevlar) for tensile protection.
- Messenger Wire: This is the defining feature. It is a high-strength, corrosion-resistant steel wire or a rigid dielectric material like FRP (Fiber Reinforced Plastic). Its primary function is to bear the entire tensile load of the aerial span, isolating the fragile optical fibers from stress, strain, and elongation.
- Integrated Jacket: A single, UV-resistant black polyethylene (PE) jacket is extruded over both the messenger and the fiber unit, binding them into a cohesive whole. The jacket material is formulated to withstand prolonged exposure to sunlight, temperature fluctuations, moisture, and abrasion. The black color provides added UV protection and helps with heat dissipation.
- Ripcord: A mandatory feature, the ripcord runs longitudinally under the jacket, allowing installers to easily access the fiber unit without damaging the fibers during splicing or termination.
This integrated design is a masterclass in functional simplicity, elegantly solving multiple installation and durability challenges in one robust package.
Key Advantages in Aerial Installation and Deployment
The true value of the bow-type drop fiber optic cable is most apparent during the installation phase. Its design directly translates into significant gains in speed, safety, and labor efficiency.
The most pronounced benefit is the dramatic reduction in installation time. Traditional methods often involve lashing a separate fiber optic cable to an existing support strand or messenger wire. This is a two-step process requiring specialized lashing equipment and more labor. In contrast, the aerial self-supporting cable design of the bow-type variant integrates the support member. The installer simply has to secure the pre-attached messenger wire to the pole or anchor points. This eliminates the lashing step altogether, cutting installation time by as much as 50%. This efficiency is a major cost-saving factor for large-scale FTTH projects where thousands of kilometers of drop cable are deployed.
Furthermore, the installation process is safer and requires less specialized skill. The procedure is more straightforward, reducing the complexity and potential for error. The cable is typically attached using standard hardware like pre-formed tension clamps or spiral vibration dampers, which are easy for linemen to apply. The integrated design also means there is no risk of the communication cable separating from the support strand over time due to failed lashing wire, a common point of failure in older systems. The low installation tension required to string the cable means lighter equipment can be used, enhancing crew safety and mobility.
Finally, the design offers exceptional versatility in span lengths. Depending on the specific construction—primarily the thickness and material of the messenger wire—bow-type drop fiber optic cable can reliably span distances between poles from 50 meters up to 150 meters or more without exceeding its maximum recommended tensile rating. This allows network planners to use existing pole infrastructure more effectively, often reducing the number of poles needed in a new build.
| Feature | Traditional Lashed Cable | Bow-Type Drop Cable | Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Installation Process | Two-step: string messenger, then lash cable | One-step: string integrated cable | Faster deployment, lower labor cost |
| Equipment Needed | Lashing equipment, tensioners, more tools | Standard pole hardware (clamps), tensioners | Simplified logistics, lower equipment cost |
| Skill Level Required | Higher, specialized training for lashing | Lower, more straightforward procedure | Easier workforce training, reduced errors |
| Typical Max Span | Varies with messenger | Consistently 50m - 150m+ | Greater design flexibility |
Superior Mechanical and Environmental Protection
Aerial cables are subjected to a relentless onslaught of environmental and mechanical stresses. The bow-type drop fiber optic cable is engineered from the ground up to endure these challenges far better than many alternative designs.
The integrated messenger wire is the first line of defense. It is designed to handle all tensile strength requirements. When the cable is tensioned between two poles, the messenger wire elongates minimally, bearing the load so that the optical fibers within the other compartment remain completely isolated from pulling force. This prevents stress-induced attenuation, a phenomenon where signal loss increases under strain, ensuring consistent network performance. The cable is also engineered to resist crushing forces during installation, such as from pole brackets or clamps, with the messenger providing a rigid backbone.
Beyond tension, aerial cables must survive constant movement. Wind-induced vibration and aeolian vibration can cause tiny, repetitive movements that lead to fatigue at support points and eventual failure in poorly designed cables. The bow-type design, often incorporating dampers or having a inherent resistance to vibration, mitigates this risk. Furthermore, the cable must handle dynamic events like ice loading and wind gusts. The robust messenger ensures the cable has the structural integrity to support additional weight without snapping or over-stretching.
The environmental protection is equally critical. The polyethylene jacket is specially compounded to be resistant to UV radiation, preventing it from becoming brittle and cracking after years of sun exposure. It is also resistant to temperature extremes, moisture, and chemicals commonly found in atmospheric pollution. For the most demanding environments, flooded cable variants are available, where a water-blocking gel fills the fiber unit, preventing any moisture ingress that could compromise the signal or freeze and damage the fibers. This comprehensive protection ensures a long service life with minimal maintenance, a key factor in reducing the total cost of ownership for the network operator.
Application-Specific Performance and Compatibility
The bow-type drop fiber optic cable is not a one-size-fits-all product but a versatile solution designed for a specific domain: the last mile connection. Its performance characteristics are perfectly matched to the demands of running from a distribution terminal on a telephone pole to a subscriber’s residence.
The use of bend-insensitive optical fiber (ITU-T G.657) is a critical feature for this application. The path from the pole to the house often requires tight bends around corners, through eaves, and into customer premises. Standard fibers can suffer from significant macro-bend losses in these scenarios, degrading the signal. Bend-insensitive fibers within the bow-type drop fiber optic cable allow for a much tighter bend radius without loss, providing installers with the flexibility needed for real-world installations and guaranteeing end-users receive the full bandwidth they are paying for.
These cables are designed for easy termination and splicing. The presence of a ripcord allows for clean and easy access to the fiber unit. The cable is typically designed for simple mid-span access, enabling a technician to break into the cable at any point to serve a subscriber without compromising the integrity of the entire run. Furthermore, its compatibility with standard pre-connectorized solutions allows for even faster installation, where a factory-terminated end can be plugged directly into a terminal, making the process almost plug-and-play and minimizing the need for highly skilled splicers on every job.
 Address:Zhong'an Road, Puzhuang Town, Suzhou City, Jiangsu Prov., China
Address:Zhong'an Road, Puzhuang Town, Suzhou City, Jiangsu Prov., China Phone:+86-189 1350 1815
Phone:+86-189 1350 1815 Tel:+86-512-66392923
Tel:+86-512-66392923 Fax:+86-512-66383830
Fax:+86-512-66383830 Email:[email protected]
Email:[email protected] Wechat: xiaobin18913501815
Wechat: xiaobin18913501815 whatsapp: +86 18913501815
whatsapp: +86 18913501815
 0
0

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español Português
Português عربى
عربى