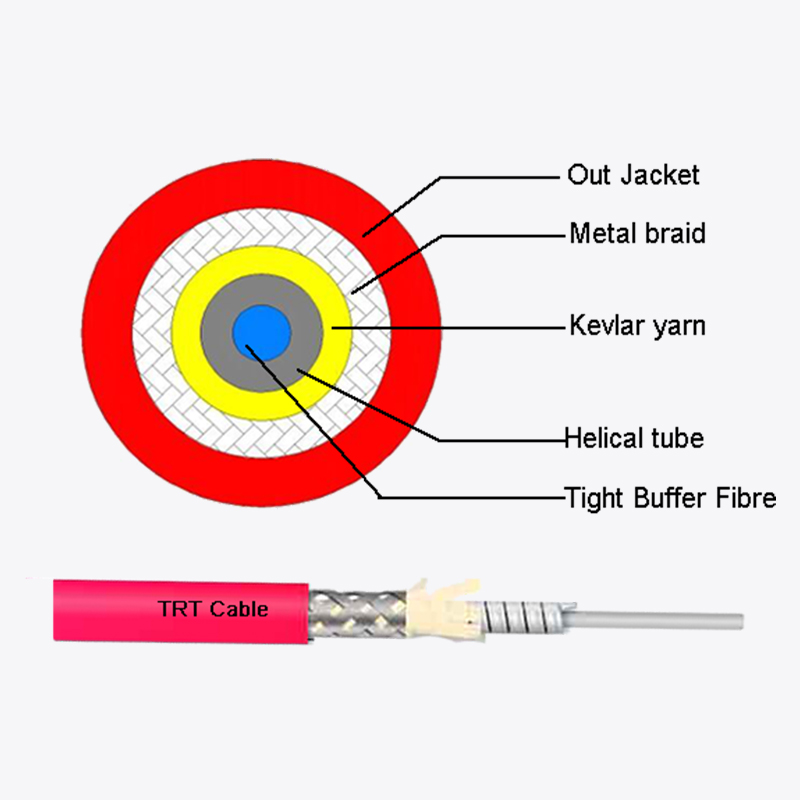
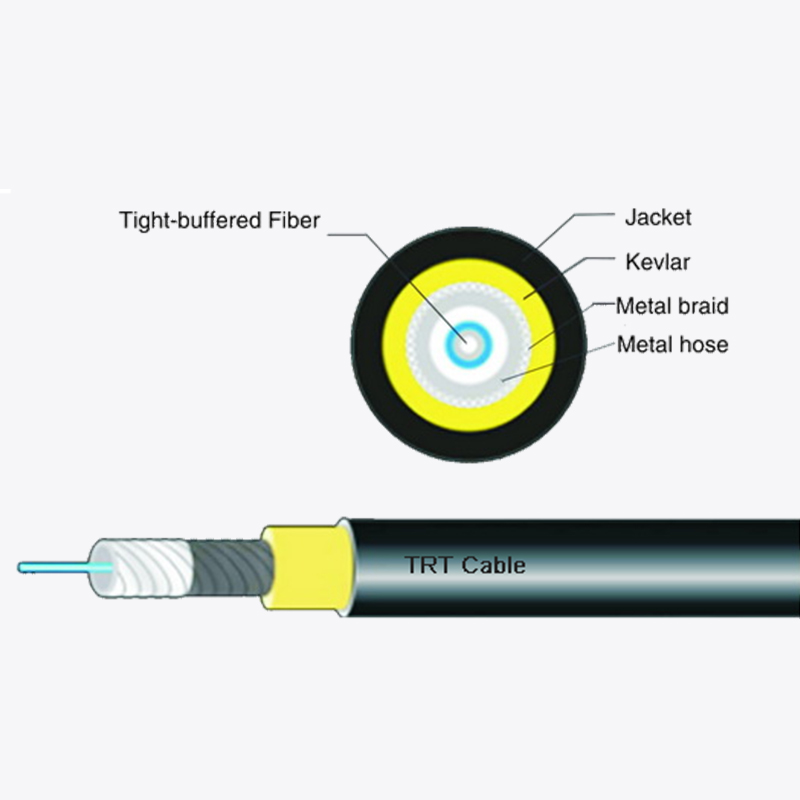
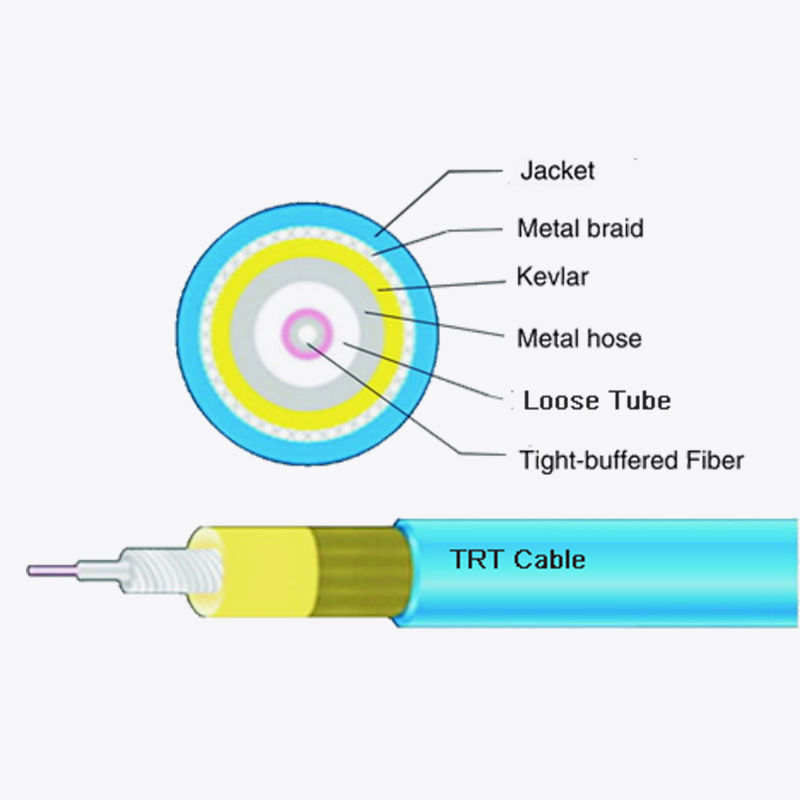
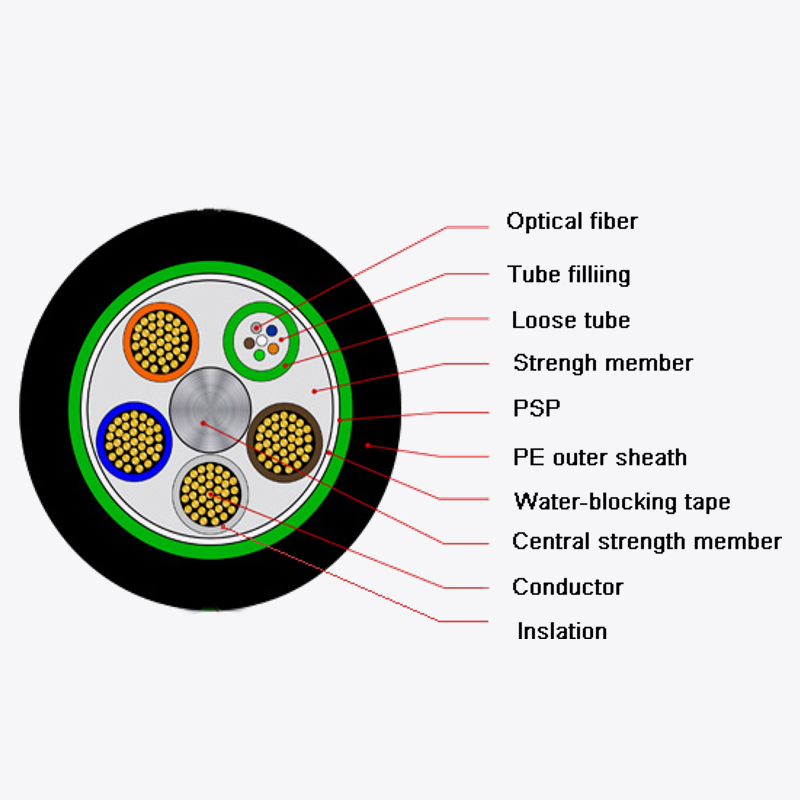
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
What Are All-Dielectric Self-Supporting (ADSS) Cables and Where Are They Used?
What Are All-Dielectric Self-Supporting (ADSS) Cables and Where Are They Used?
Fiber optic cables have become the backbone of modern communication and power transmission networks, offering high bandwidth, low latency, and resistance to electromagnetic interference. Among the various types of aerial fiber optic cables, the all-dielectric self-supporting (ADSS) cable stands out due to its unique design and versatility. Unlike traditional cables that require separate messenger wires for support, ADSS cables are engineered to bear their own weight while withstanding environmental stresses.
Understanding ADSS Cables: Design and Key Features
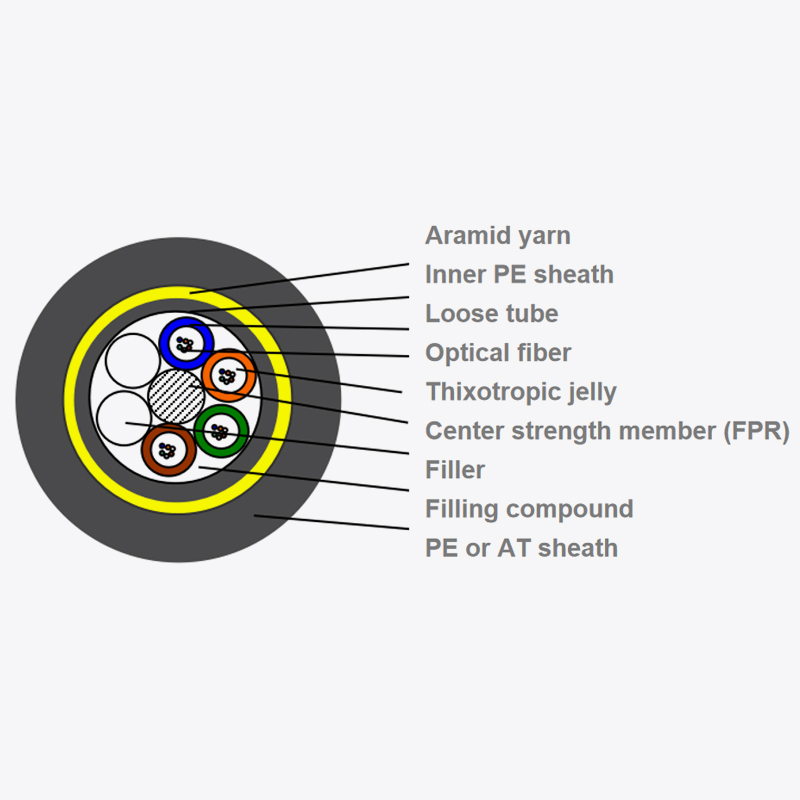
ADSS cables are designed for aerial deployment without the need for external support structures. Their all-dielectric construction means they contain no metallic components, making them immune to electromagnetic interference and corrosion—a critical advantage in power line and telecommunications applications.
The cable’s core consists of optical fibers surrounded by protective layers, including water-blocking materials and strength members. The most common reinforcing elements are aramid yarns or fiberglass rods, which provide the necessary tensile strength to span long distances between utility poles or transmission towers. An outer sheath, typically made of weather-resistant polyethylene (PE) or tracking-resistant material, protects against UV radiation, moisture, and pollution.
One of the defining characteristics of ADSS cables is their self-supporting capability. Unlike conventional fiber optic cables that rely on steel messenger wires, ADSS cables integrate load-bearing components within their structure. This design simplifies installation and reduces the need for additional hardware, lowering both material and labor costs.
Why Choose ADSS? Benefits and Key Applications
ADSS cables offer several advantages that make them a preferred choice for aerial installations. Their lightweight yet durable construction allows for deployment in diverse environments, including urban areas, rural landscapes, and harsh weather conditions. Since they do not conduct electricity, they can be safely installed near high-voltage power lines without risk of induced currents.
Primary Applications
-
Telecommunications Networks
- ADSS cables are widely used in fiber-to-the-home (FTTH), backbone networks, and mobile backhaul for 5G infrastructure. Their ability to follow existing power line routes reduces the need for new right-of-way acquisitions, accelerating deployment.
-
Power Utility Communications
- Electric utilities use ADSS cables for supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, grid monitoring, and fault detection. Their non-conductive nature ensures safe operation even when strung alongside high-voltage transmission lines.
-
Smart Grid and Renewable Energy Integration
- As power grids modernize, ADSS cables facilitate real-time data transfer between substations, wind farms, and solar plants, supporting smart grid automation and distributed energy resource management.
Compared to traditional optical ground wire (OPGW) or lashed fiber cables, ADSS cables provide easier retrofitting on existing poles without structural reinforcements. Their flexibility in installation makes them ideal for projects requiring rapid deployment with minimal disruption.
Installation and Deployment Best Practices
While ADSS cables simplify aerial installations, proper deployment requires careful planning to ensure long-term reliability. Key considerations include:
Environmental and Mechanical Factors
- Span Length and Sag: The distance between support structures must be calculated to prevent excessive tension or sag, which could lead to fiber strain or cable damage.
- Wind and Ice Loads: In regions prone to severe weather, engineers must account for additional stresses caused by wind pressure and ice accumulation.
- Pole and Tower Compatibility: Existing infrastructure must be assessed to confirm it can handle the additional load, especially when adding ADSS cables to power lines.
Safety and Compliance
ADSS installations must adhere to industry standards such as IEEE, IEC, or utility-specific guidelines. Proper grounding, although not required for the cable itself, may be necessary for hardware attachments. Additionally, workers must follow safety protocols when installing cables near live power lines to prevent accidents.
Proper installation techniques—such as avoiding sharp bends, maintaining minimum bend radius, and using appropriate suspension clamps—ensure optimal performance and longevity.
The Future of ADSS Cables: Trends and Innovations
As demand for high-speed connectivity and resilient power grids grows, ADSS technology continues to evolve. Key developments include:
Enhanced Materials for Durability
New sheath materials with improved UV resistance, hydrophobicity, and pollution resistance are being tested to extend cable lifespan in extreme climates. Some manufacturers are exploring nanocomposite coatings to further reduce environmental degradation.
Higher Tension Capacity
Research into advanced aramid fiber blends and carbon-reinforced components aims to increase tensile strength, allowing for longer spans and reduced mid-span supports.
Expanding Role in 5G and Smart Cities
With the rollout of 5G networks and smart city initiatives, ADSS cables will play a crucial role in connecting small cells, IoT devices, and distributed antenna systems (DAS). Their ability to leverage existing utility infrastructure makes them a cost-effective solution for dense urban deployments.
Integration with Renewable Energy Projects
As wind and solar farms expand, ADSS cables provide reliable communication links for remote monitoring and control, supporting the transition to sustainable energy systems.
ADSS cables represent a versatile and efficient solution for aerial fiber optic deployments, combining durability, ease of installation, and immunity to electromagnetic interference. Their applications span telecommunications, power utilities, and smart infrastructure, making them a critical component in modern connectivity and grid management. As material science advances and network demands increase, ADSS technology will continue to adapt, reinforcing its role in the future of high-speed data and energy transmission.
 Address:Zhong'an Road, Puzhuang Town, Suzhou City, Jiangsu Prov., China
Address:Zhong'an Road, Puzhuang Town, Suzhou City, Jiangsu Prov., China Phone:+86-189 1350 1815
Phone:+86-189 1350 1815 Tel:+86-512-66392923
Tel:+86-512-66392923 Fax:+86-512-66383830
Fax:+86-512-66383830 Email:[email protected]
Email:[email protected] Wechat: xiaobin18913501815
Wechat: xiaobin18913501815 whatsapp: +86 18913501815
whatsapp: +86 18913501815
 0
0

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español Português
Português عربى
عربى