Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
How does the tensile strength of bow-type drop fiber optic cable compare to other cables?
How does the tensile strength of bow-type drop fiber optic cable compare to other cables?
Fiber optic cables are critical components in modern telecommunications, and their mechanical properties, particularly tensile strength, play a significant role in ensuring reliable performance. Among the various types of fiber optic cables, bow-type drop fiber optic cable is widely used in last-mile connectivity, such as fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) deployments. A key consideration when selecting a cable for these applications is its ability to withstand pulling forces during installation and environmental stress afterward.
Understanding tensile strength in fiber optic cables
Tensile strength refers to the maximum load a cable can endure before breaking or suffering permanent deformation. For fiber optic cables, this is crucial because excessive tension can lead to signal loss, fiber breaks, or increased attenuation. The bow-type drop fiber optic cable is designed with a robust structure to handle installation stresses, particularly in aerial and outdoor environments. Unlike loose-tube or armored cables, which are built for long-haul or harsh conditions, bow-type drop cables prioritize flexibility and lightweight construction while maintaining sufficient tensile strength for short-distance deployments.
Structural differences affecting tensile strength
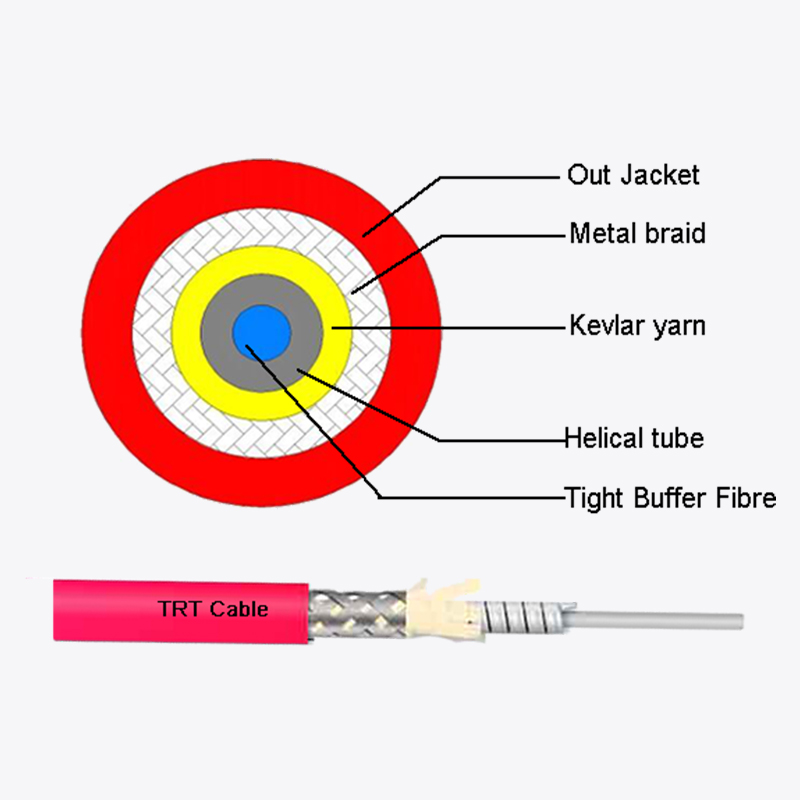
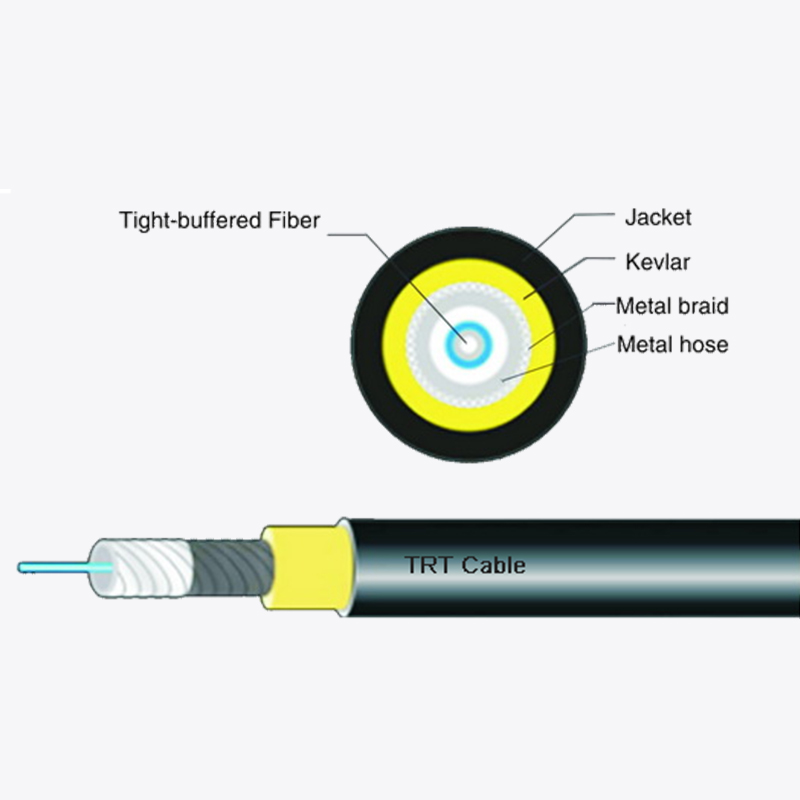
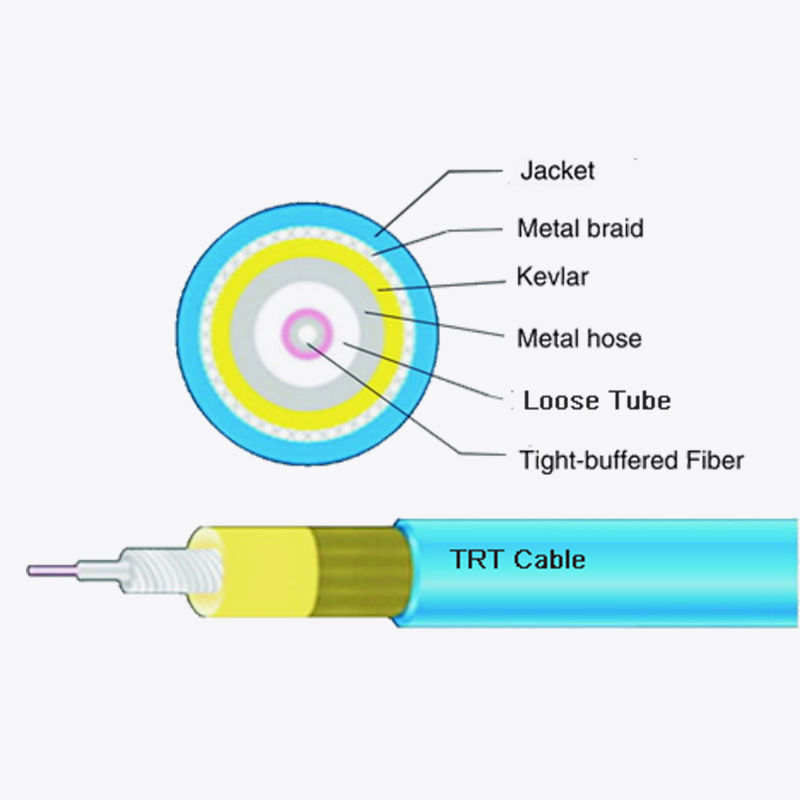
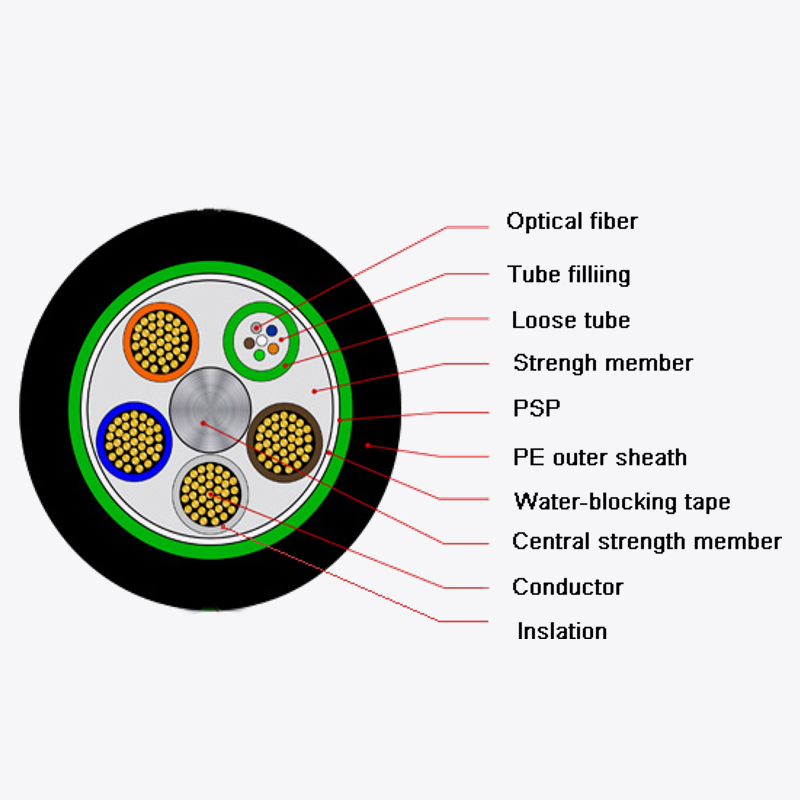
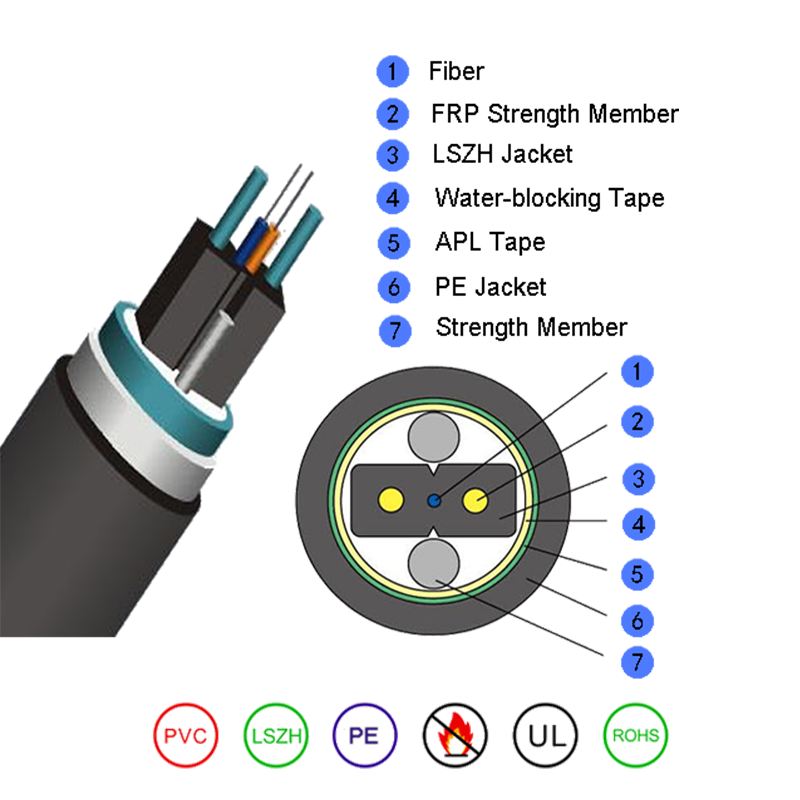
The tensile strength of bow-type drop fiber optic cable is influenced by its unique construction. Typically, it features a central strength member, often made of fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP) or aramid yarn, which provides resistance to stretching. The optical fibers are arranged around this member, and an outer jacket protects against environmental factors. In contrast, other cables, such as loose-tube cables, use additional strength elements like steel wires for higher tensile resistance, making them suitable for underground or direct-burial applications. Meanwhile, tight-buffered cables, often used indoors, rely on thicker coatings around individual fibers rather than external strength members, resulting in lower tensile strength compared to bow-type drop cables.
The following table summarizes the typical tensile strength ranges for different fiber optic cable types:
| Cable Type | Typical Tensile Strength Range | Primary Strengthening Element |
|---|---|---|
| Bow-type drop fiber optic cable | 100–600 N | FRP or aramid yarn |
| Loose-tube cable | 600–2,000 N | Steel wire or rod |
| Tight-buffered cable | 50–200 N | Thick fiber coating |
| Armored cable | 1,000–4,000 N | Corrugated steel or aluminum |
Performance under installation and operational stress
The tensile strength of bow-type drop fiber optic cable is optimized for aerial and drop installations, where cables are subject to tension during stringing between poles or buildings. While it may not match the extreme tensile resistance of armored or loose-tube cables, it provides a balanced combination of strength and flexibility. This makes it ideal for FTTH deployments, where cables must navigate tight bends and withstand wind loads without excessive sagging.
In comparison, loose-tube cables are built for higher tensile loads, making them suitable for long-span aerial installations or underground ducts where pulling forces are more intense. However, their rigidity can be a drawback in last-mile scenarios where flexibility is needed. On the other hand, tight-buffered cables, while easy to handle indoors, lack the tensile strength required for outdoor use, limiting their application to controlled environments.
Environmental and long-term durability
Another factor influencing tensile performance is environmental exposure. The bow-type drop fiber optic cable is designed to resist UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations, which can degrade materials over time and reduce tensile strength. The use of weather-resistant jackets and corrosion-resistant strength members ensures that the cable maintains its integrity even after prolonged outdoor exposure.
In contrast, armored cables, while offering superior tensile strength, may be prone to corrosion if the metal components are not properly protected. Similarly, tight-buffered cables may experience jacket degradation when used outdoors, leading to a decline in tensile performance. Thus, while some cables may have higher initial tensile strength, their long-term durability must also be considered.
The tensile strength of bow-type drop fiber optic cable is well-suited for its intended applications, striking a balance between durability and flexibility. While it does not match the extreme tensile resistance of armored or loose-tube cables, it outperforms tight-buffered cables in outdoor and aerial installations. The choice of cable depends on the specific deployment requirements, including installation method, environmental conditions, and expected mechanical stresses. Bow-type drop fiber optic cable remains a reliable solution for FTTH and last-mile connectivity, offering sufficient tensile strength for most drop cable applications while maintaining ease of handling and cost-effectiveness.
 Address:Zhong'an Road, Puzhuang Town, Suzhou City, Jiangsu Prov., China
Address:Zhong'an Road, Puzhuang Town, Suzhou City, Jiangsu Prov., China Phone:+86-189 1350 1815
Phone:+86-189 1350 1815 Tel:+86-512-66392923
Tel:+86-512-66392923 Fax:+86-512-66383830
Fax:+86-512-66383830 Email:[email protected]
Email:[email protected] Wechat: xiaobin18913501815
Wechat: xiaobin18913501815 whatsapp: +86 18913501815
whatsapp: +86 18913501815
 0
0

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español Português
Português عربى
عربى